- About
- News
- Faculty
-
Academics
- School of Physical Science and Technology (SPST)
- School of Life Science and Technology (SLST)
- School of Information Science and Technology (SIST)
- School of Entrepreneurship and Management (SEM)
- School of Creativity and Art (SCA)
- Institute of Humanities (IH)
- School of Biomedical Engineering (BME)
- Shanghai Institute for Advanced Immunochemical Studies (SIAIS)
- iHuman Institute
- Institute of Mathematical Sciences (IMS)
- Center for Transformative Science (CTS)
- Institute of Carbon Neutrality (ICN)
- Shanghai Clinical Research and Trial Center
- Tech Transfer
- Global
- Campus Life
-
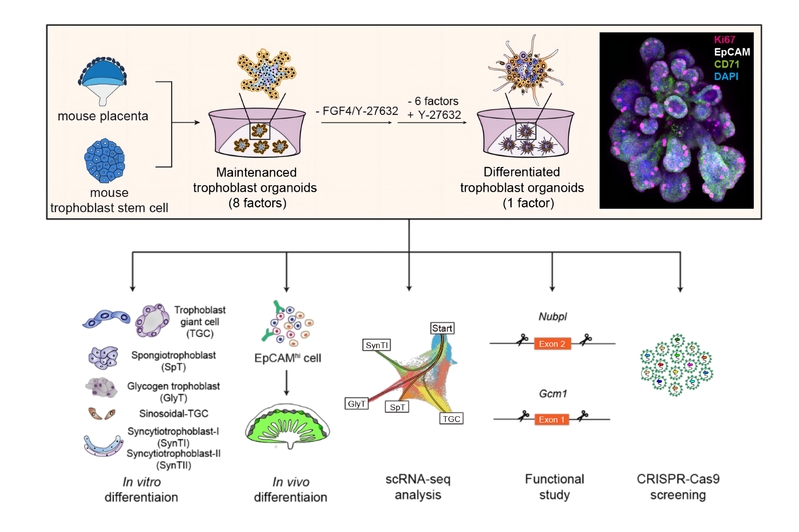 Through a 100-million-year evolution and adaptation, the eutherian placentae has become one ofthe most morphologically variable organs. Besides the fetal-maternal exchange, recent studies in mouse models have demonstrated that developmental defects in placentae could exert pronounced effects on embryo growth and development, leading to the necessity for high-throughput screens on modulators for mo...
Through a 100-million-year evolution and adaptation, the eutherian placentae has become one ofthe most morphologically variable organs. Besides the fetal-maternal exchange, recent studies in mouse models have demonstrated that developmental defects in placentae could exert pronounced effects on embryo growth and development, leading to the necessity for high-throughput screens on modulators for mo... -
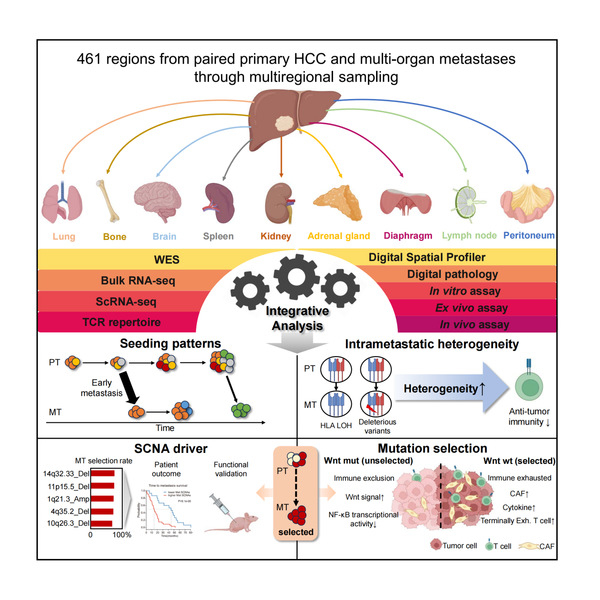 Hepatocellular carcinoma, a highly prevalent malignant tumor in China, accounts for nearly half of the newly diagnosed cases and deaths worldwide annually. Among liver cancer patients, 70-80% are diagnosed with tumor spread and metastasis, rendering them ineligible for surgical intervention. However, a comprehensive understanding of the molecular characteristics specific to metastatic liver cancer...
Hepatocellular carcinoma, a highly prevalent malignant tumor in China, accounts for nearly half of the newly diagnosed cases and deaths worldwide annually. Among liver cancer patients, 70-80% are diagnosed with tumor spread and metastasis, rendering them ineligible for surgical intervention. However, a comprehensive understanding of the molecular characteristics specific to metastatic liver cancer... -
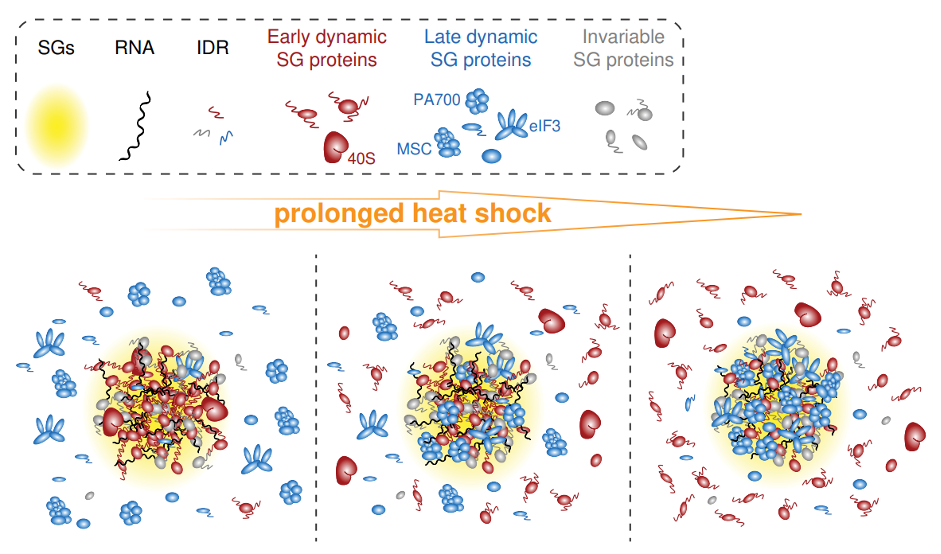 Stress granules (SGs) are membrane-less organelles that transiently arise in the cytoplasm in response to adverse environmental conditions. They form through liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS). SGs are thought to regulate mRNA functions during stress and participate in cell-fate specification by orchestrating the depletion and release of cytosolic regulatory proteins. Much effort has been focus...
Stress granules (SGs) are membrane-less organelles that transiently arise in the cytoplasm in response to adverse environmental conditions. They form through liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS). SGs are thought to regulate mRNA functions during stress and participate in cell-fate specification by orchestrating the depletion and release of cytosolic regulatory proteins. Much effort has been focus... -
 CorrectSequence Therapeutics (Correctseq), a biotechnology company incubated from ShanghaiTech using innovative base editing technology to help people with severe diseases, today announced that the company and the research teams from ShanghaiTech University, Wuhan University, Fudan University and Children’s Hospital of Fudan University published an article entitled “Base editing of the HBG ...
CorrectSequence Therapeutics (Correctseq), a biotechnology company incubated from ShanghaiTech using innovative base editing technology to help people with severe diseases, today announced that the company and the research teams from ShanghaiTech University, Wuhan University, Fudan University and Children’s Hospital of Fudan University published an article entitled “Base editing of the HBG ... -
 Methamphetamine (METH), commonly known as crystal meth, is one of the most abused substances, posing a serious burden on human health and society. Currently, there are no approved drugs available for the treatment of METH addiction. METH addiction primarily operates by modulating dopamine release and reuptake, a widely known mechanism. Recent studies indicated that METH can directly bind to Trace ...
Methamphetamine (METH), commonly known as crystal meth, is one of the most abused substances, posing a serious burden on human health and society. Currently, there are no approved drugs available for the treatment of METH addiction. METH addiction primarily operates by modulating dopamine release and reuptake, a widely known mechanism. Recent studies indicated that METH can directly bind to Trace ... -
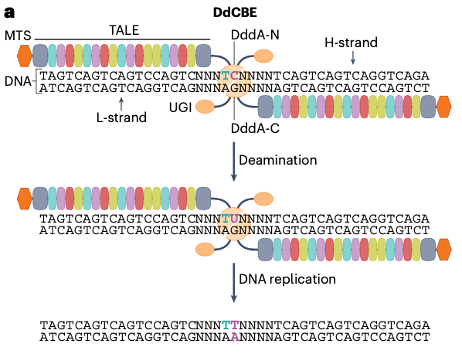 Mitochondria and chloroplasts are organelles that include their own genomes, which encode key genes for ATP production and for carbon dioxide fixation, respectively (Fig. 1). Mutations in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) can cause diverse genetic disorders and are also linked to aging and age-related diseases, including cancer. Targeted editing of organellar DNA should be useful for studying organellar g...
Mitochondria and chloroplasts are organelles that include their own genomes, which encode key genes for ATP production and for carbon dioxide fixation, respectively (Fig. 1). Mutations in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) can cause diverse genetic disorders and are also linked to aging and age-related diseases, including cancer. Targeted editing of organellar DNA should be useful for studying organellar g... -
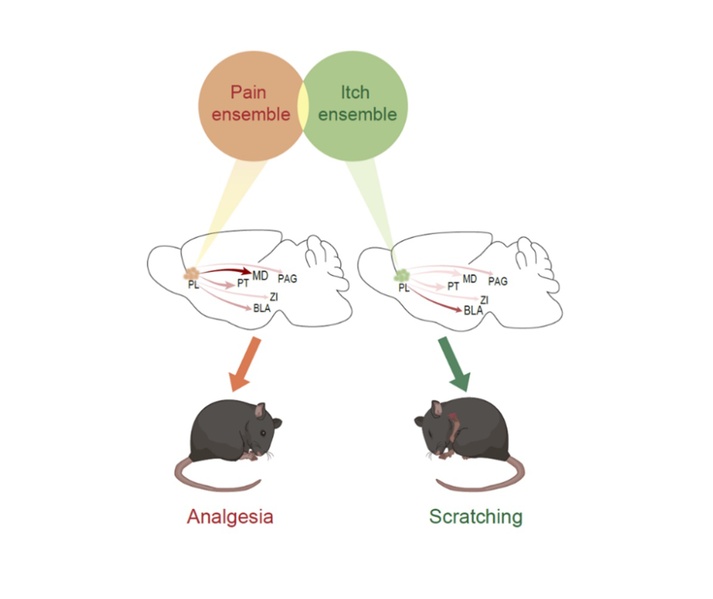 The ability to detect harmful stimuli through biological testing is crucial for an individual’s survival. Pain and itch, as essential components of the body’s somatic sensations, aid in defending against external nociceptive stimuli and prevent tissue damage. Despite sharing similar neuroanatomical pathways and involvement in the development of related chronic diseases, pain and itch are fu...
The ability to detect harmful stimuli through biological testing is crucial for an individual’s survival. Pain and itch, as essential components of the body’s somatic sensations, aid in defending against external nociceptive stimuli and prevent tissue damage. Despite sharing similar neuroanatomical pathways and involvement in the development of related chronic diseases, pain and itch are fu... -
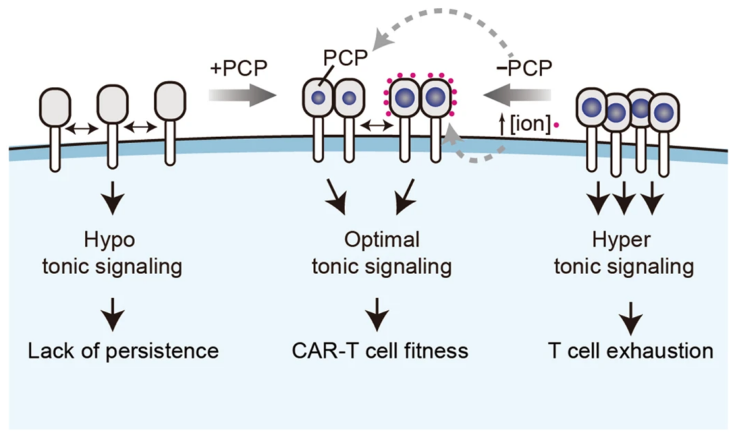 CAR-T cell therapy is a tumor immunotherapy that activates the expression of Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) on patients’ T cells, enabling them to recognize and kill tumor cells. CAR-T therapy has shown remarkable efficacy against blood cancers but poor efficacy against solid tumors. One of the primary reasons is that the tonic signal of CAR-T cells leads to their exhaustion. Recent studies...
CAR-T cell therapy is a tumor immunotherapy that activates the expression of Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) on patients’ T cells, enabling them to recognize and kill tumor cells. CAR-T therapy has shown remarkable efficacy against blood cancers but poor efficacy against solid tumors. One of the primary reasons is that the tonic signal of CAR-T cells leads to their exhaustion. Recent studies... -
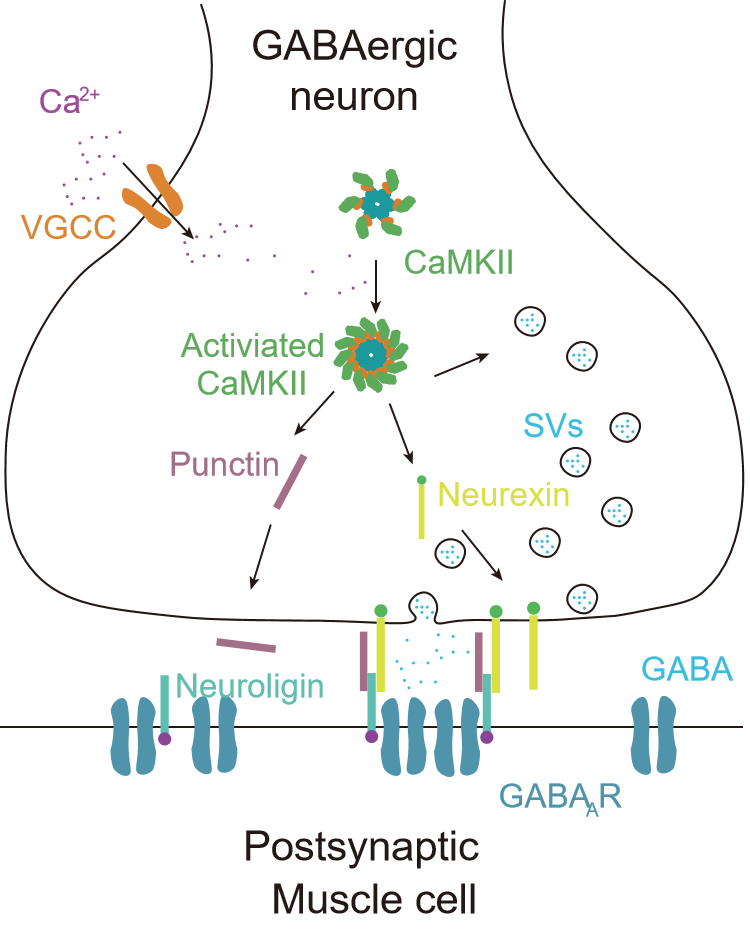 Synapse is the contact between neurons where information passes through. According to the types of information, there are excitatory and inhibitory synapses, and the inhibitory synaptic transmission plays a pivotal role in maintaining the excitatory and inhibitory balance. Disturbance of inhibitory synaptic transmission has been reported relevant to many neurodevelopmental and psychiatric disorder...
Synapse is the contact between neurons where information passes through. According to the types of information, there are excitatory and inhibitory synapses, and the inhibitory synaptic transmission plays a pivotal role in maintaining the excitatory and inhibitory balance. Disturbance of inhibitory synaptic transmission has been reported relevant to many neurodevelopmental and psychiatric disorder... -
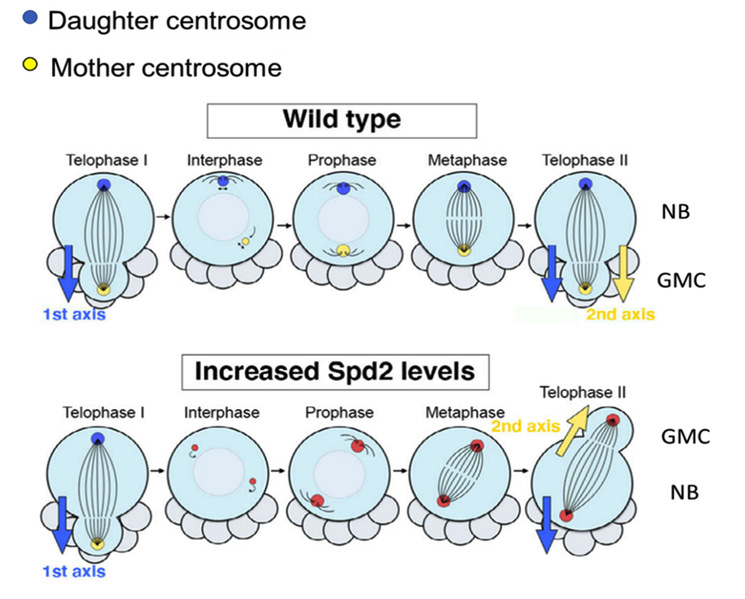 In multicellular organisms, the centrosome plays a critical role in development and tissue homeostasis. In various early embryos and stem cells, the centrosome regulates their polarized or asymmetric cell division. Centrosome dysfunction is linked to various diseases including cancer, microcephaly and ciliopathy. APC/C (Anaphase-Promotion Complex/cyclosome) is an evolutionarily conserved ubiquitin...
In multicellular organisms, the centrosome plays a critical role in development and tissue homeostasis. In various early embryos and stem cells, the centrosome regulates their polarized or asymmetric cell division. Centrosome dysfunction is linked to various diseases including cancer, microcephaly and ciliopathy. APC/C (Anaphase-Promotion Complex/cyclosome) is an evolutionarily conserved ubiquitin... -
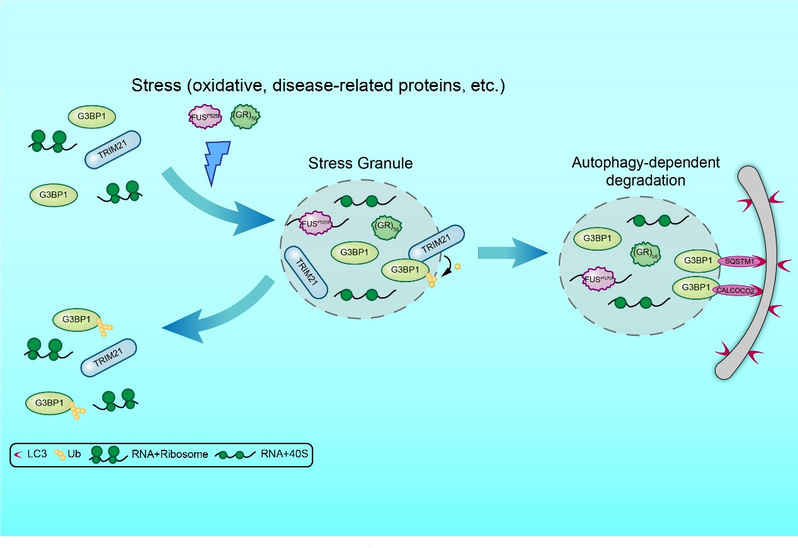 Stress granules are membraneless condensates of RNA and RNA-binding proteins formed in response to cell stress. New evidence of the relationship between stress granules and neurodegenerative diseases highlights their physiological importance. Therefore, understanding the mechanism of this association and determining the key players that control stress granule homeostasis are crucial to t...
Stress granules are membraneless condensates of RNA and RNA-binding proteins formed in response to cell stress. New evidence of the relationship between stress granules and neurodegenerative diseases highlights their physiological importance. Therefore, understanding the mechanism of this association and determining the key players that control stress granule homeostasis are crucial to t... -
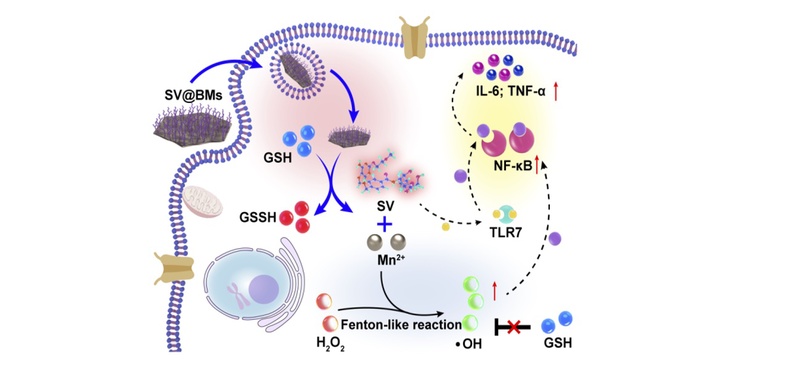 Osteosarcoma is the most common primary malignant tumor of bone, mostly seen in children and adolescents. Comprehensive treatment options for osteosarcoma have not evolved significantly in the last 30 years, and there is an urgent need to explore new therapies. Osteosarcoma is highly malignant, prone to metastasis, and has a poor prognosis. Traditional standard treatment of osteosarcoma relie...
Osteosarcoma is the most common primary malignant tumor of bone, mostly seen in children and adolescents. Comprehensive treatment options for osteosarcoma have not evolved significantly in the last 30 years, and there is an urgent need to explore new therapies. Osteosarcoma is highly malignant, prone to metastasis, and has a poor prognosis. Traditional standard treatment of osteosarcoma relie... -
 In November, Life Dean's Lecture of ShanghaiTech came again as scheduled. The Life Dean's Lecture is a special edition of the SLST Seminar held once a year, where distinguished experts in life sciences are invited to share the frontier scientific advances with faculty and students. This year, James Rothman, winner of the 2013 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine and Distinguished Adjunct ...
In November, Life Dean's Lecture of ShanghaiTech came again as scheduled. The Life Dean's Lecture is a special edition of the SLST Seminar held once a year, where distinguished experts in life sciences are invited to share the frontier scientific advances with faculty and students. This year, James Rothman, winner of the 2013 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine and Distinguished Adjunct ... -
 As an important small molecule metabolite, NAD+ is widely involved in a series of biochemical reactions in cell energy metabolism, such as glycolysis, oxidative phosphorylation, and fatty acid oxidation. Tumor cells proliferate faster and are prone to DNA damage, requiring more NAD+ consumption. NAMPT is a key rate-limiting enzyme for NAD+ synthesis. Aberrant overexpression of NAMPT...
As an important small molecule metabolite, NAD+ is widely involved in a series of biochemical reactions in cell energy metabolism, such as glycolysis, oxidative phosphorylation, and fatty acid oxidation. Tumor cells proliferate faster and are prone to DNA damage, requiring more NAD+ consumption. NAMPT is a key rate-limiting enzyme for NAD+ synthesis. Aberrant overexpression of NAMPT...
- per page 14 records total 92 records
- firstpage <<previouspage nextpage>> endpage
- PageNumber 1/7 jumpto

